Objectives of this lecture
Understand what is ‘Complete Spatial Randomness’ and ‘Spatial Patterns’
To learn how to identify Clustering Pattern
Grid-based, counting: Quadrat Count Analysis
Distance-based, sorting: Nearest Neighbor Analysis
Distance-based, searching: Ripley’s K-function(s)
Monte-Carlo Simulation
Two Types Clustering in Spatial Analysis¶
some parts of the study area that have very high concentration of point events, i.e., ‘clusters’
to check if this phenomenon exists in the spatial point data
to identify the location of these clusters
significant tests, CSR
groups of spatial points that are close to each other, i.e., ‘clusters’
identify grouping of points with/without overlap
Three Major types of Point Pattern¶
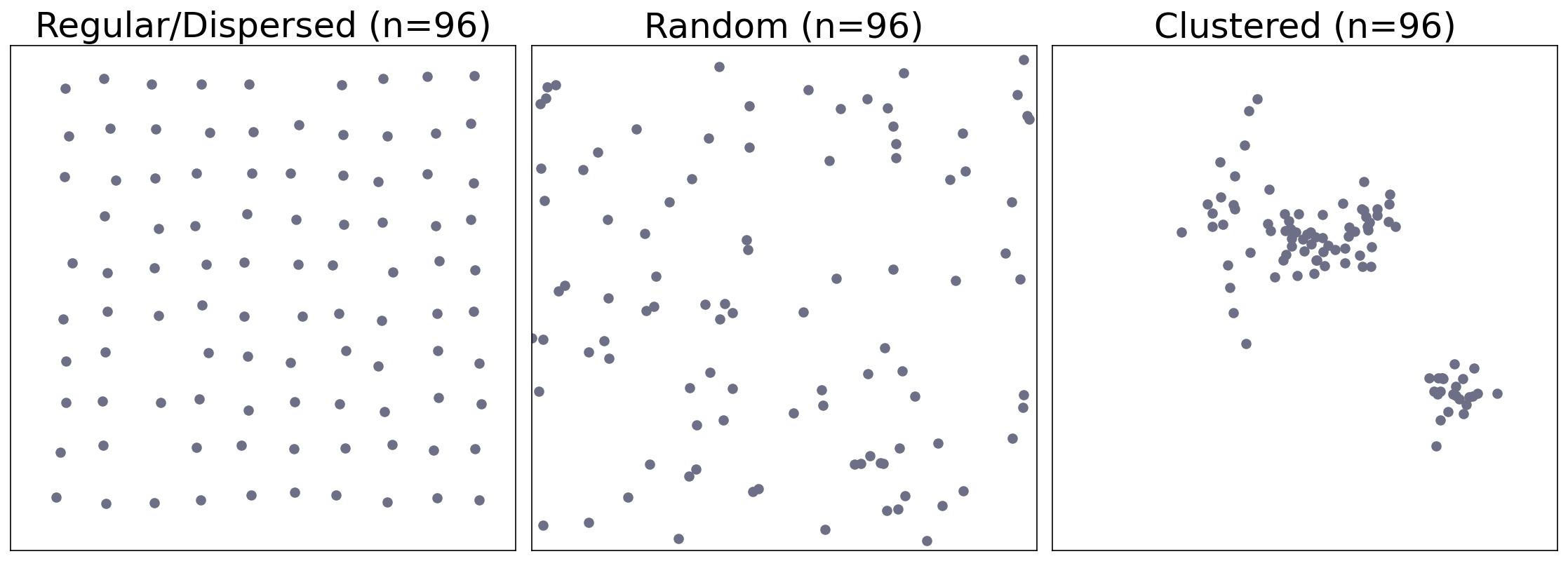
Regular, random, and clustered.
How to differentiate clustered from random (CSR)?
CSR: Complete Spatial Randomness
Measurement strategies¶
Grid-based
Distance-based
Grid-based¶
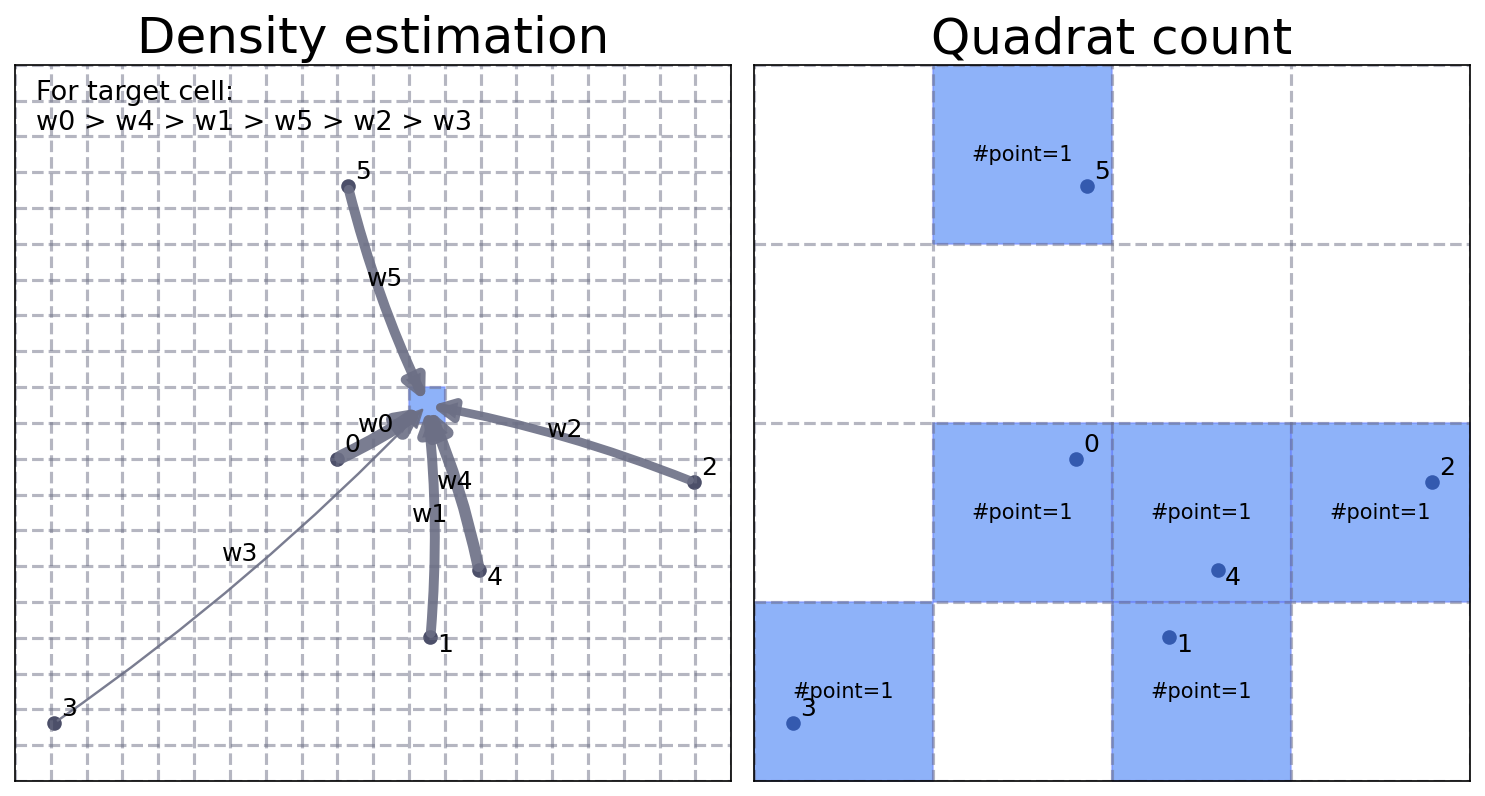
Grid-based: density estimation and quadrat count.
Distance-based¶
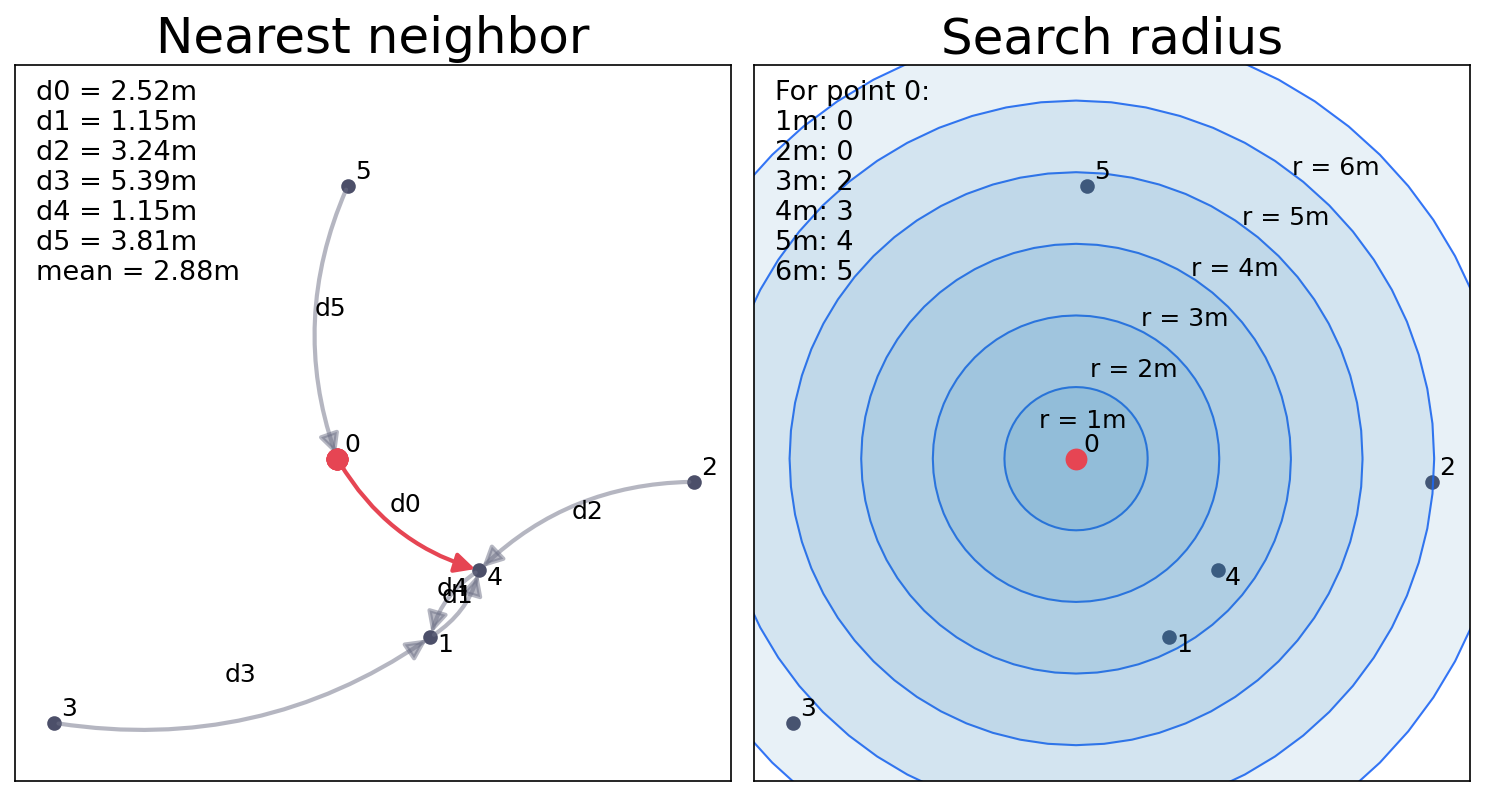
Distance-based: search for the k-nearest and find neighbors fall within a search-radius (buffer).