What do you think is the first step of data analysis?
Yes, it is Data Preprocessing
About Data Preprocessing¶
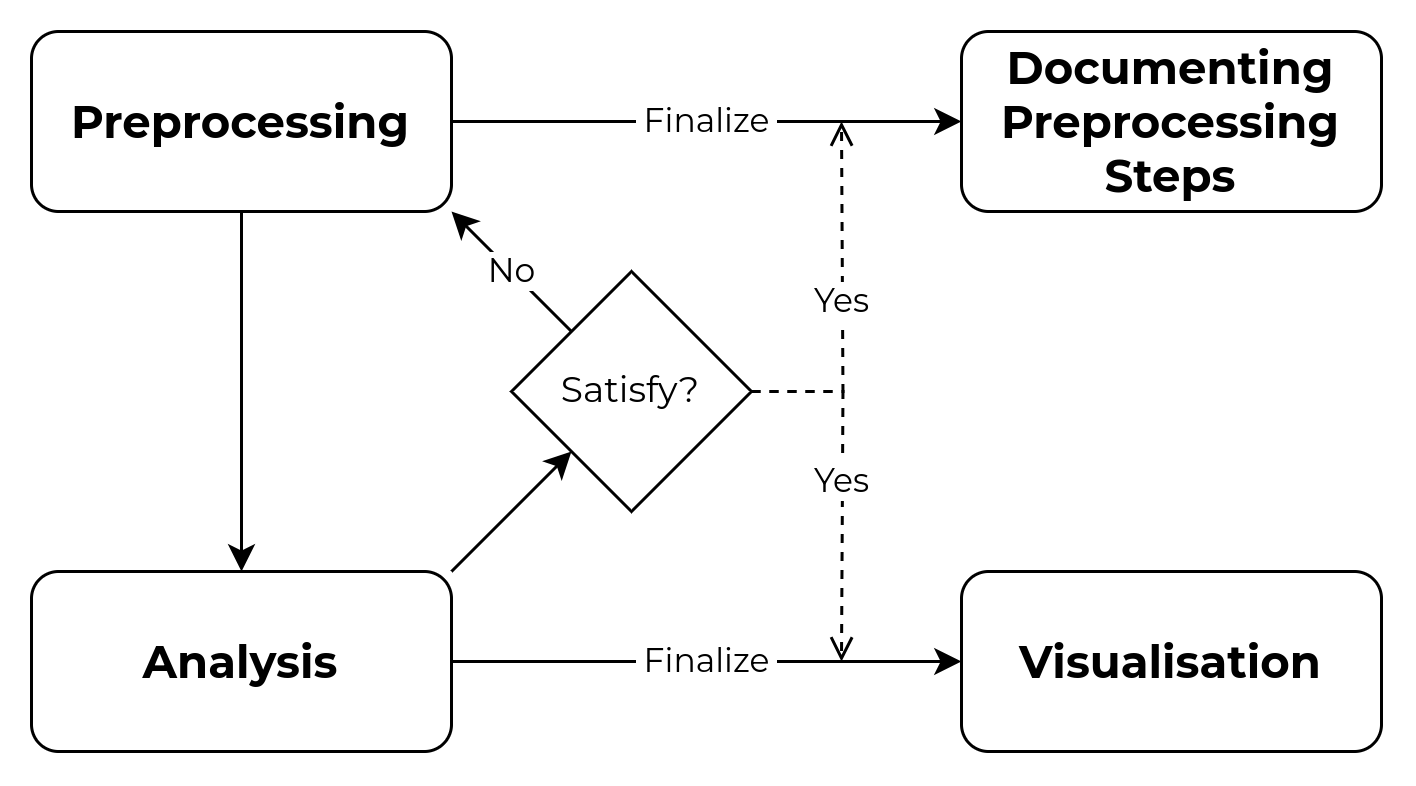
Key data preprocessing process.
What to do after data collection
Identifying structure
Cleaning and Editing
Coding
Classification
Transcription
Alignment
Tabulation
Transformation
Initial analysis
The steps are not sequential. Sometimes, some steps are done repeatedly, concurrently, and iteratively.
Identifying structure¶
Look at the patterns
What is/was the purpose for data collection?
What is the design strategy of data collection?
What is the structure/organization of the collected data?
Any expectations? Counter-intuitive patterns?
Is there any (expected/unexpected) relationships between variables?
Is there any (expected/unexpected) hierarchies?
Is there any (expected/unexpected) groupings?
Data Cleaning & Editing¶
Remove errors.
Remove inconsistencies.
Resolve duplicate entries.
What to do with missing values (default values, inputation, interpolation, deletion)?
What to do with outliers?
Verify accuracy of individual data points.
Ensure data is complete and consistent.
Use manual editing or automated data validation techniques.
Correct typos or formatting issues.
Documenting: write down the steps you took.
Coding¶
Assign codes to qualitative data (e.g., survey responses), e.g.,
yes/no, true/false to 1 and 0 (or 1 and 2)
male/female to 1 and 0 (or 1 and 2)
ordered data, e.g., Very disagree, slightly disagree, neutral, slightly agree, very agree, to numbers (-2 to 2, or 0 to 4), etc.
categorical data, e.g., land use, land cover, urban functional zones, house types, to numbers (nominal).
Create new variables based on existing ones, e.g.,
calculating age from year of birth,
5 yo age groups from age,
income levels from gross income,
measuring differences (differences of magnitude vs. magnitude of differences).
Use consistent coding schemes across various data sources.
*Documenting: write down the code definitions and rules. *
Classification¶
Organize data into predefined categories or classes.
Define classification criteria or rules:
at what level of household income could be considered as ‘high’/‘medium’/‘low’ income
how many times a month can be considered high frequency
Apply classification methods consistently:
natural break, head-tail break, quantiles, etc.
Evaluate classification validity, accuracy and consistency.
Documenting: write down the classification method and your reason.
Transcription¶
(mainly for qualitative data collection approach)
Convert audio to text using speech-to-text software.
Transcribe video content to text format.
Extract text from images using OCR (Optical Character Recognition).
Perform manual or automated transcription as needed.
Alignment¶
Standardize formats, naming conventions, spatial scales, and units of measurement.
Ensure compatibility between different data sources.
Make sure the projections and anchor points are same.
Handle inconsistencies in data representation or encoding.
Documenting: write down data alignment decisions and procedures.
Tabulation¶
Summarize data into tables or cross-tabulations.
Create join-able tables:
unique identifiers/keys for every person/location
split tables for participants’ background, participants’ perspective on XXX, participants’ performance
Facilitate exploratory data analysis (EDA) and reporting.
Create pivot tables or aggregated data views.
Present data in a clear and concise format.
Transformation¶
Apply appropriate transformations
Address skewness, non-linearity, or differing scales.
Perform tests as needed (statistics assumptions for further analyses, etc.).
Normalize or standardize data as needed.
Monitor impact on data distribution and relationships.
Documenting: write down the steps and reasons.
Initial analysis¶
Perform exploratory data analysis (EDA) to gain insights.
Identify trends, patterns, or relationships in the data.
Check assumptions for further analysis or modeling.
Generate visualizations (e.g., histograms, scatter plots) to support EDA.
Summary¶
Identifying structure: Looking for patterns
Cleaning and Editing: Identifying and resolving issues
Coding: Assigning values and meanings
Classification: Grouping and categorizing data
Transcription: Extracting relevant information
Alignment: Standardizing data formats
Tabulation: Creating a structured view of data
Transformation: Manipulating data for analysis
Initial analysis: Exploring patterns and trends
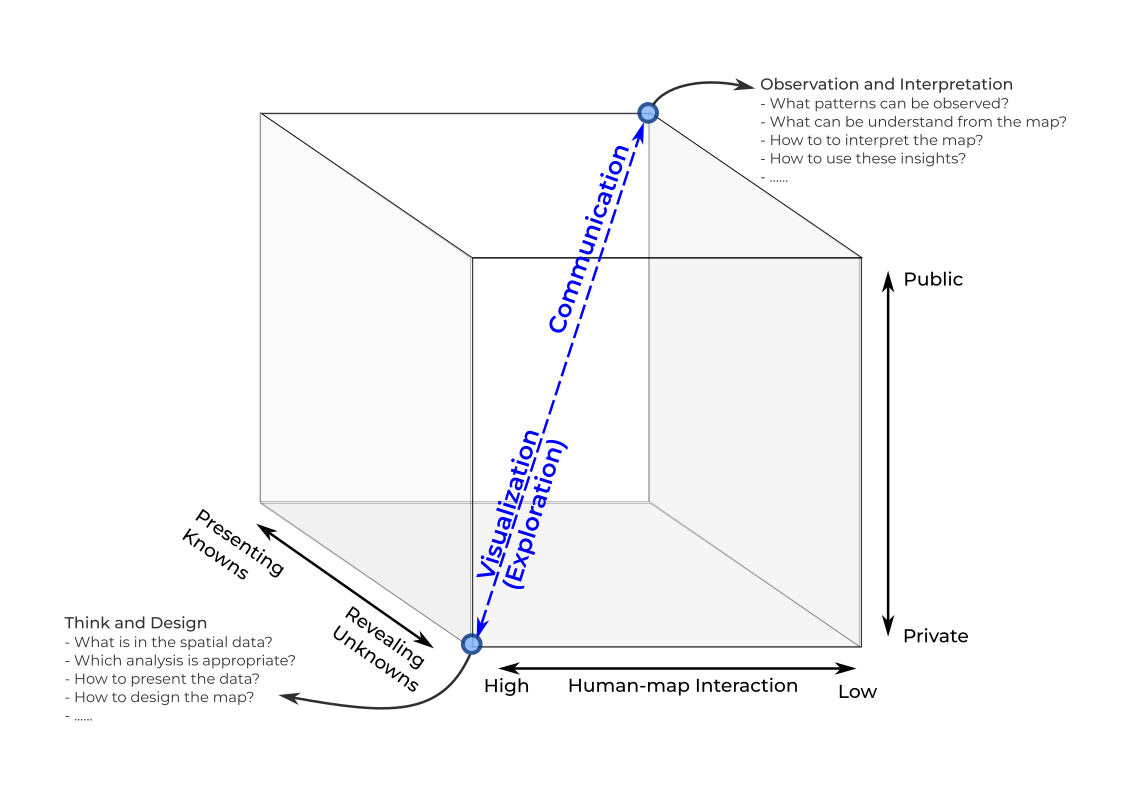
MacEachren’s cartographic cube. In the exploring steps (lower left corner).